Monday, November 2, 2009
Treatment of lungs cancer for people who smooking
Thursday, October 29, 2009
Best Hospital For Cancer Treatment In Pakistan
The service & treatment is best becouse the enviroment of this hospital is clean. & its good for health of people.
Sunday, October 11, 2009
How Much Cancer Is Making Problems In Our Life
Sunday, September 6, 2009
Doctors advice for cancer peoples
doctors also give advice to eat freash and healthy food becouse freash food makes your body fit & healthy.
Tuesday, June 16, 2009
Types of Breast Cancer
When breast cancer spreads outside the breast, cancer cells are often found in the lymph nodes under the arm (axillary lymph nodes). If the cancer has reached these nodes, it may mean that cancer cells have spread to other parts of the body--other lymph nodes and other organs, such as the bones, liver, or lungs--via the lymphatic system or the bloodstream.
Cancer that spreads is the same disease and has the same name as the original (primary) cancer. When breast cancer spreads, it is called metastatic breast cancer, even though the secondary tumor is in another organ. Doctors sometimes call this "distant" disease.
Sunday, June 14, 2009
Brain Cancer
A cancer diagnosis can be frightening, but especially so when there's a tumor in the brain. While some types of brain cancer or cancer in the brain are less aggressive than others, all have the potential to disrupt a person's thoughts, memories, senses, personality, language abilities, and body control. And brain cancer can be life threatening, particularly if left untreated.
Like any other cancer, brain cancer or cancer in the brain gets its start when cells start dividing abnormally and uncontrollably, forming growths known as tumors. But not all tumors are cancerous. Some are benign, meaning that they are caused by overgrowth of normal cells.
Benign tumors tend to grow slowly and don't spread, or metastasize, in the same way that malignant tumors do. Still, benign tumors in the brain or spinal cord can pose a threat to health because they can compress and destroy adjacent vital tissue or increase pressure in the skull.
Cancerous tumors in the brain typically don't spread to distant areas of the body, but they can invade other areas of the brain and the spinal cord.
The Primary brain tumors are classified according to the type of brain cells they develop from, the appearance of individual cells under the microscope, their location in the brain, or a combination of these factors. More than half of adult brain tumors are gliomas, which mean they arise in the tissue in the brain known as glial tissue. Examples include astrocytomas, which start in brain cells called astrocytes, and glioblastomas, which are particularly aggressive forms of astrocytomas.
In terms of successful treatment, more important than the name of the tumor is its GRADE, the term used to describe a tumor's aggressiveness or how likely it is to grow. Grade 1 tumors tend to look more like normal cells and grow slowly and rarely spread, giving patients an excellent chance at long-term survival. Grade 2 tumors also grow relatively slowly, but they can creep into nearby brain tissue. These tumors can come back if removed, sometimes as a higher-grade tumor.
Grade 3 tumors are much like grade 2, but they grow slightly more quickly and are more likely to recur. Grade 4 tumors are the most dangerous: the cancer cells reproduce rapidly and, if left unchecked, will quickly invade other parts of the brain or spinal cord. Very rarely, grade 4 tumors can spread beyond the nervous system to other parts of the body.
Cause of Brain Cancer
Scientists don't completely understand why brain cells turn cancerous, but some factors can make the disease more likely. Radiation to the head, given as a form of treatment for brain tumors, can increase the risk of brain cancers.

Exposure to vinyl chloride (an odorless gas used in the manufacturing of plastics), petroleum products, and certain other chemicals have been linked to an increased risk. Research is still in progress to check if certain viruses trigger the disease. The disease rarely strikes more than one member of a family, although rare cases of certain types of brain cancers do run in families.
Contrary to popular belief, there is still no clear evidence at this point that cellular phones, power lines, or aspartame can cause brain cancer.
Brain cancer can arise at any age, but most patients are either younger than 12 or older than 40. Slightly more than one-fourth of all brain tumors are primary. The remaining is secondary (metastatic). It's not known what causes primary brain tumors. It's possible that heredity, environmental factors, viruses or other factors play a role in their development.
Some common types of primary tumors which are named after the type of brain cells from which they originate include acoustic neuromas (schwannomas), astrocytomas, medulloblastomas, meningiomas and oligodendrogliomas.
Secondary (metastatic) brain tumors are tumors that result from brain cancer that starts elsewhere in the body and then spreads (metastasizes) to the brain. Cancers of the lung and breast are most likely to spread to the brain. Sometimes, a brain tumor is the first sign of cancer that began elsewhere in the body.
HPV Test: The Best Method In Determining The Cervical Cancer!
 Human papilloma virus is a dangerous infection which can cause cervical caner in women.
Human papilloma virus is a dangerous infection which can cause cervical caner in women.
The only way to prevent this virus is having HPV test to be done, which can easily determine the presence of HPV virus in your body.
Generally women above 35 years of age are recommended to have HPV test.
How cervical cancer is related to HPV?
Human papilloma virus is a virus which is mainly responsible for the growth of abnormal cells on the surface of cervix.
There are more than 100 different species of HPV virus in which about five strains mainly cause the cervical cancer.
These group of viruses infect your body and causes genital warts. The most common way of identifying the HPV infection is genital warts. These warts can be very small, depending on the severity of the infection.
Mostly these viruses are not active and long enough to cause the infection. On the other hand, if the HPV virus is of high risk type, then it can lead to cervical cancer by developing abnormal cells on the cervix.
Cone Biopsy - Best Method In Detecting Cervical Disorders!
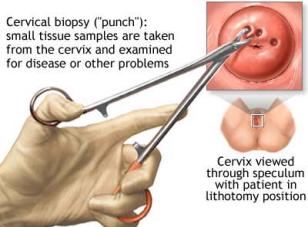 Are you suffering with cervical disorder or cervical cancer?
Are you suffering with cervical disorder or cervical cancer?
Cone biopsy is the surgery which will help in removing the tumors which are responsible for cervical disorders.
Cervical cancer is the common problem for most of the women. It mainly shows its effect on your reproductive system.
Cone biopsy is an extensive method of cervical biopsy.
In this method, a piece of tissue which is cylindrical in shape is taken for the diagnosis of the cervical cancer. Small tumors in the cervix can be removed with cone biopsy.
Cone biopsy is generally recommended for two main purposes:
- It is used to take the thin or thick sample tissues inside the cervix, which is needed for diagnosis of the cervical cancer.
- It is also used for the treatment of some abnormal tissues or tumors present inside the cervix, which does not need any long term treatment or surgeries to be removed.
Cone biopsy is usually done in either of two given ways:
- LEEP, loop electrosurgical excision procedure is one of the surgical methods of cone biopsy, in which the tissue is removed with the help of an electric wire, heated with an electric current. In this method of surgery, you will be given only with local anesthesia and it is a quick process which can be done at your physician’s office.
HPV Test To Detect The Risk Of Developing Cervical Cancer
HPV test (Human Papillomavirus Test) is also known as a high-risk HPV test. The HPV test is performed on a sample of cells collected from the cervix.
This test makes use of advanced, automated technology to detect the presence of high risk or oncogenic strains of HPV virus, the primary underlying factor in the development of cervical cancer.
HPV Test - The Best Predictor Of Cervical Cancer!
 The Pap smear test reporting ASCUS (atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance) is a major concern in cervical cancer screening.
The Pap smear test reporting ASCUS (atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance) is a major concern in cervical cancer screening.
A Pap test resulting ASCUS refers to a mild abnormality in the cervix.
Most of the Pap-detected mild abnormalities go away without any treatment.
As Pap smear may not clarify the abnormality until cancer has developed, the doctor cannot make sure which abnormality go away and which is more serious (pre-cancer or cancer) for treatment [Cervical cancer treatment].
Fortunately, now there is a test called HPV test, which helps clarify the Pap smear-detected abnormalities and the necessity of treatment. It also provides helpful information that can decide how soon the next Pap test should be and the need of other tests.
Rates Of Cervical Cancer Rising Among Teens
 Bad news for teenage girls: while rates of cervical cancer are going down in women over 25, among 15 to 19-year-olds, rates are rising year on year.
Bad news for teenage girls: while rates of cervical cancer are going down in women over 25, among 15 to 19-year-olds, rates are rising year on year.
Jillian Birch, at the University of Manchester, UK, and her colleagues examined national cancer incidence data and looked specifically at young people aged 15 to 24.
They noticed that between 1979 and 2003, the incidence of cervical cancer had increased by 1.6% per year. When they examined the data more closely, they found that people aged 15 to 19 were driving that increase, with the rate going up 6.8%, Birch told the Teenage Cancer Trust’s fifth international conference in London today.
Previous studies indicate that most women who get infected with the virus contract it in their teens or early 20s. But while many women are simply able to clear the virus, and others develop a slow-growing cancer decades later, when cervical cancer appears in young women it can develop rapidly.
Mouth Cancer
Mouth cancer or Cancer of the mouth usually starts in the cells lining the mouth. The most common sites are the lips, tongue and floor of the mouth, but cancer can also originate in the gums, cheeks, roof of the mouth, hard and soft palate, tonsils and salivary glands.
People over the age of 45 years are at increased risk, with men twice as likely as women to develop these types of cancers.
Smoking increases the risk of mouth cancer six-fold. The location of the mouth cancer seems to depend on the usage of the tobacco product – for example, a person who habitually tucks plugs of chewing tobacco into their left cheek may be prone to cancer of that cheek.
 Heavy alcohol consumption increases the risk of mouth cancer even more. Mouth cancer is easily cured if treated in its earlier stages, but around half of patients don’t consult with their doctor until their disease is well advanced.
Heavy alcohol consumption increases the risk of mouth cancer even more. Mouth cancer is easily cured if treated in its earlier stages, but around half of patients don’t consult with their doctor until their disease is well advanced.
Saturday, June 13, 2009
Ovarian cancer
Our unique one-strand Ovarian Cancer Bracelet is made with large blue zircon Swarovski crystals and Bali silver beads.
You can promote ovarian cancer awareness by wearing our simple, but elegant Ovarian Cancer Bracelet. Our Ovarian Cancer Bracelet is the perfect gift for a ovarian cancer survivor or to commemorate a loved one who lost their fight with ovarian cancer.
What is Ovarian Cancer?
Ovarian cancer is very aggressive. It is the fifth most common cancer in women. It is diagnosed in more than 25,000 women in the United States each year, and approximately 16,000 women die of the disease annually. The median age is 56, but it has been seen in women as young as 22. Classic symptoms include a bloated or enlarged abdomen, urinary urgency, constipation and/or diarrhea. It is most often misdiagnosed as Irritable Bowel Syndrome.
The CA-125 Blood Test is a simple test that detects ovarian cancer. While many doctors offices and even insurance companies will tell you they have never heard of it, if pressed, the test is covered by insurance. If you are experiencing the above symptoms, do not take "no" for an answer.
How can I reduce my risk of ovarian cancer?
-Use of oral contraceptives
-Having at least one child
-Breast-feeding a child for a year or longer
-Tubal ligation or hysterectomy
Eating well, managing stress and exercise are all great ways to promote your overall health and combat ovarian cancer.
Support ovarian cancer awareness by purchasing an Ovarian Cancer Bracelet today.
Treatment of cervical cancer
If the biopsy shows that you have cancer, your doctor will do a thorough pelvic exam and may remove additional tissue to learn the extent (stage) of your disease. The stage tells whether the tumor has invaded nearby tissues, whether the cancer has spread and, if so, to what parts of the body.
These are the stages of cervical cancer:
- Stage 0: The cancer is found only in the top layer of cells in the tissue that lines the cervix. Stage 0 is also called carcinoma in situ.
- Stage I: The cancer has invaded the cervix beneath the top layer of cells. It is found only in the cervix.
- Stage II: The cancer extends beyond the cervix into nearby tissues. It extends to the upper part of the vagina. The cancer does not invade the lower third of the vagina or the pelvic wall (the lining of the part of the body between the hips).
- Stage III: The cancer extends to the lower part of the vagina. It also may have spread to the pelvic wall and nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage IV: The cancer has spread to the bladder, rectum, or other parts of the body.
- Recurrent cancer: The cancer was treated, but has returned after a period of time during which it could not be detected. The cancer may show up again in the cervix or in other parts of the body.
Pancreatic Cancer
the pancreas is a gland that makes insulin and hormones, plus digestive enzymes. Pancreatic cancer develops from the ducts carrying the digestive juices. The organ is described as having three parts: head, body and tail of pancreas.
Cancer spreads from lymph nodes to liver, lungs, peritoneum. 32 000 cases per year in the US , with poor prognosis, because of late discovery and very difficult surgical access.
2) Risk factors of pancreatic cancer:
- some food factors, such as sugar, coffee abuse;
- favoured with tobacco, diabetes, often preceded by chronic pancreatitis;
- more men than women are concerned (2 to 1); the mean age is 65; African Americans more than Asians
or whites.
3) Growth:
pancreatic cancer is often associated with stomach cancer, the proximity of these organs making it difficult to establish the original cancer.
4) Symptoms:
- the most frequent sign is jaundice, caused by compression of the bile duct which crosses the pancreas: dark
urine, yellow skin, yellow eyes, pale stool, itching;
- weakness, weight loss, nausea;
- stabbing pains in across the upper abdomen.
5) Diagnosis of pancreatic cancer:
- clinical exam: signs for jaundice, liver cirrhosis;
- transabdominal ultrasound; endoscopy; retrograde cholangiopancreatography, with biopsies; scanner.
- the tumor marker assays: CEA , CA 19-9.
6) Treatment:
- surgery: depending on the localization on the pancreas, the size, the stage. The head of pancreas can be removed, part of small intestine, stomach, gallbladder, spleen. This is a major operation and very delicate surgery, that can be attempted if the tumor is resectable and if there are no metastases.
- radiation and chemotherapy, in cases of non resectable tumors, can lead to some remissions.
7) Follow-up:
using the tumor marker dosages.
8) Prevention:
- diabetes appropriate monitoring;
- no-tobacco use (once again);
- tumor marker test.
The above-mentioned tumor markers are part of the Biomarkers C12 test; performing this panel once a year is highly recommended.
Cancer can be detected : do it NOW.
Testicular Cancer
Testicular cancer prevention can be done with routine physical test by health professor or by self examination.
Health professor has to be consulted immediately when you have any discomfort in pelvis, lower back or scrotum.
For testicular cancer prevention, two methods are observed. They are:
- Testicular treatment and
- Testicular self-examination
Tests are conducted to detect the testis abnormalities or lumps. The male reproductive organs are testes that are present inside the scrotum which produce the sperms and testosterone, a hormone.
Their shape and size is same as an egg. A coiled tube called epididymis is at the back of testis that collects the sperms and stores them.
In the abdomen, the testis develops and before or after the birth, it descends into the scrotum. There will be increase in risk factor if the testis is not descended.
Testicular examination is the physical examination of the genital organs and groin done by the health professor. The presence of swelling, any visual signs of abnormalities, lumps or shrinking testis can be examined by the heath professor by feeling your organs.
Inflammation, pain, swelling, masses or lumps and congenital abnormalities in you are detected by the testicular examination for the presence of any testicular cancer.
The genital examination for any man or boy irrespective of age is important. The genitals should be examined in your babies for the undescended testis and congenital abnormalities.
For the detection of early-stage testicular cancer, the testicular examination is done in men between the ages 15 to 40 years. It occurs mostly in younger men than older one. If you are having early stage testicular cancer, it can be treated easily and can be cured fastly.
Testicular self examination (TSE) is used to detect the early stage testicular cancer. The testicular cancers are discovered as enlarged testis and lumps with out pain by the self-examination.
If your age is between 15 and 40 years, then you are recommended to have testicular self-examination monthly by the health professor.
But it is controversial. Monthly TSE is not needed for men with low risk of developing the testicular cancer. It is necessary for the men with high risk for developing this cancer. The risk factor can involve the family history of undescended testis and personal history of this cancer.
Immediate treatment is required if you have cancerous testicular lumps. The treatments used for testicular cancer prevention are surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
Surgery is done to remove the affected testis. The lymph nodes are also removed. For this purpose, the chemotherapy and radiation therapy are used.
Artificial testis is inserted into the scrotum for normal appearance. Your reproductive system is not affected as there is one normal testis.
Testicular cancer prevention is possible by Testicular treatment and Testicular self-examination.
Liver Cancer Information
The incidence of liver cancer in the United States is currently estimated at around 3 per 100,000 persons, with significant gender, ethnic and geographic variations. However, these numbers are rising quickly and may be a gross under-estimate. For reasons that are not really clear, it is a predominantly male disease with a male:female ratio of 4:1.
Although all the causes of liver cancers are not known, we do know that the majority are caused by hepatitis B, hepatitis C and/or abuse of alcohol. Those factors typically lead to cirrhosis, which in turns leads to liver failure and/or liver cancer (HCC). Depending on the part of the world, dietary contamination may also be important. In the United States, obesity has recently been shown to be important in the development of cirrhosis, a predisposing factor to the development of HCC. (If you have one or more of these risk factors, speak with your physician about proactive screening tests.)
Lungs Cancer

The lungs are an essential life force for our bodies. The body cannot survive without the lungs ability to draw life-sustaining oxygen from the air and expel toxic carbon dioxide. The oxygen supplied by the lungs is necessary for the proper functioning of all our body's cells. Therefore, alterations in that ability affect every part of the body.
Each lung is divided into lobes. Unlike other body parts, the lungs are not an exact match. The right lung is divided into three lobesupper, middle and lower. The left lung has two lobes- upper and lower. Each of these lobes functions as a mini-lung. This unique quality allows surgeons to remove one or more lobes, as is sometimes necessary for lung cancer treatment, leaving the remaining lobes unaffected and capable of sustaining life.
The center of the chest is called the mediastinum. This is the part of the body that contains the heart, major blood vessels, lymph nodes and the esophagus. Pulmonary arteries and veins are responsible for carrying blood to and from the lungs. The pleura is a slippery membrane that lines your chest cavity and covers each of your lungs to allow the lungs to move smoothly.
Inhalation delivers air to the lungs via the bronchial tree which consists of the trachea (wind pipe) and branches out into two bronchi leading to each lung. The branches continue into a tree like structure inside the lungs referred to as the bronchial tubes or bronchioles. There are more than 300 million alveoli, clusters of microscopic air sacs, contained at the ends of the bronchioles. The alveoli are responsible for the transferring of oxygen and carbon dioxide. As cells receive oxygen, they release carbon dioxide and other toxic substances into the blood stream. Carbon dioxide then passes from small blood vessels called capillaries into the alveoli. When we exhale we expel carbon dioxide into the air. With our next breath the entire process begins again.
Prostate cancer
The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system located just below the bladder (the organ that collects and empties urine) and in front of the rectum (the lower part of the intestine). It is about the size of a walnut and surrounds part of the urethra (the tube that empties urine from the bladder). The prostate gland produces fluid that makes up part of semen.
 |
| Anatomy of the male reproductive and urinary systems, showing the prostate, testicles, bladder, and other organs. |
As men age, the prostate may get bigger. A bigger prostate may block the flow of urine from the bladder and cause problems with sexual function. This condition is called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), and although it is not cancer, surgery may be needed to correct it. The symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia or of other problems in the prostate may be similar to symptoms of prostate cancer.
 |
| Normal prostate and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). A normal prostate does not block the flow of urine from the bladder. An enlarged prostate presses on the bladder and urethra and blocks the flow of urine. |
Skin Cancer Prevention: 5 Ways to Protect Yourself from UV Rays
Skin cancer comes in three forms: basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and malignant melanoma. Of the three, melanoma is the most dangerous and life threatening. Skin cancer claims the lives of approximately ten thousand Americans on an annual basis.
What causes skin cancer??
Overexposure to ultraviolet sunlight (UV rays) is believed to be the dominant external factor in a person’s development of skin cancer, although genetic factors can play a role. To protect yourself from UV rays, you should take the following 5 steps for proper skin cancer prevention:
1. Avoid Direct Sun Exposure: Avoid exposing your skin to direct sunlight during midday (generally from 10am to 4pm). This is the time when UV rays are most intense. Plan your schedule to avoid outdoor activities during these hours. Also, be aware that sand and snow reflect sunlight, so if you’re at the beach or a ski resort, direct sunlight can bombard you from every direction with UV rays.
2. Cover Yourself: When out in the sun, keep your skin covered. Wear long-sleeves and long pants if possible. Wearing a hat with a 3 to 4 inch brim all around is preferable. This will guard your neck and cheeks from dangerous prolonged exposure. Also note that dry, dark-colored garments offer the best protection.
3. Use Sunscreen Properly: You should always use sunscreen when enduring prolonged exposure in the sun. Find a sunscreen with a Sun Protection Factor of at least 15 and read the directions for proper application. The higher the SPF, the higher the protection you will receive against dangerous sunburns. However, sunscreen does not offer “bulletproof” protection, and UV rays can penetrate water, so just because you feel “cool” in the water doesn’t mean you’re protected from sunburn.
4. Use Sunglasses That Block UV Rays: Making certain your sunglasses can block UV rays helps to guard your eyes from serious sun damage. The best constructed sunglasses should have a UV ray absorption rate of 99% to 100%. Never assume that darker lenses equal increased protection. UV rays are blocked by a chemical applied to the lenses. This chemical has nothing to do with the color of transparency of sunglass lenses.
5. Stay Away From Tanning Beds: It is a myth to believe that tanning beds and sunlamps are free of harmful UV rays. These cosmetic instruments might make your skin more attractive in the short-term, but they can significantly increase your risk of developing skin cancer in the long-term. Health professionals advise their patients to avoid them.
By implementing these 5 steps in your daily routine, you can significantly decrease your risk of developing skin cancer, while maintaining a healthy lifestyle that allows for proper exposure to the sun. Another important step in prevention of skin cancer is routine examination by a doctor. If skin cancer is detected early, then your odds of survival are markedly increased.
Wednesday, June 10, 2009
Breast Cancer Symptoms


-A breast lump or breast mass noted upon breast exam -- usually painless, firm to hard, and usually with irregular borders
-Lump in the armpit
-A change in the size or shape of the breast
-Abnormal nipple discharge: Usually bloody or clear-to-yellow or green fluid
-Change in the color or feel of the skin of the breast, nipple, or areola: Dimpled, puckered,
Retraction, "orange peel" appearance; Redness;
- veins on breast surface
-Change in appearance of the nipple - enlargement or itching
-Breast pain, enlargement or discomfort on one side only
-Symptoms of advanced disease are bone pain, weight loss, swelling of one arm, skin ulceration.


